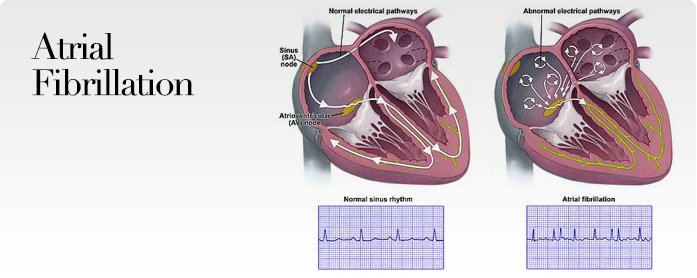
| Atrial fibrillation is an arrhythmia in which the upper chambers of the heart do not contract in a co-ordinated fashion, and the lower chambers contract irregularly. The pulse feels completely irregular and may be very rapid or very slow. |
|
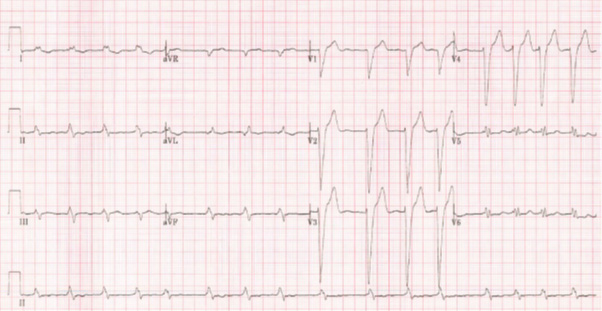
| This is an ECG showing atrial fibrillation |
|
 |
|
| SYMPTOMS OF ATRIAL FIBRILLATION |
- Palpitations
- Giddiness or fainting
- Breathlessness
- Chest discomfort
- Stroke
- Leg and abdominal swelling
|
|
| COMPLICATIONS OF ATRIAL FIBRILLATION |
- Heart failure
- Stroke
|
|
| CONDITIONS ASSOCIATED WITH ATRIAL FIBRILLATION |
- Hypertension
- Heart valve disease
- Cardiomyopathy
- Coronary artery disease
- Congenital heart disease
- Thyrotoxicosis
- Chronic lung disease
- Sick Sinus Syndrome
- After any open heart surgery (first 1 month)
|
|
| TREATMENT OF ATRIAL FIBRILLATION |
|
| Treatment is directed at: |
- Control of heart rate
- Correction of heart rhythm
- Prevention of stroke
|
|
| Control of heart rate |
- Drugs
- Catheter ablation and pacemaker implantation
|
|
| Correction of heart rhythm |
- Drugs
- Electrical Cardioversion
- Catheter ablation
|
|
| Prevention of stroke |
- Aspirin or clopidogrel
- Warfarin
- Dabigatran or Rivaroxaban or Apixaban or Edoxaban
|