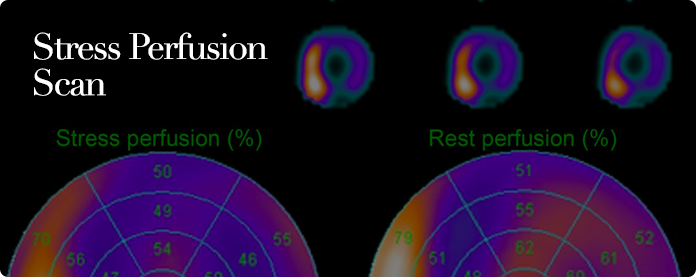
| Stress testing is used to detect the presence of coronary artery disease. |
|
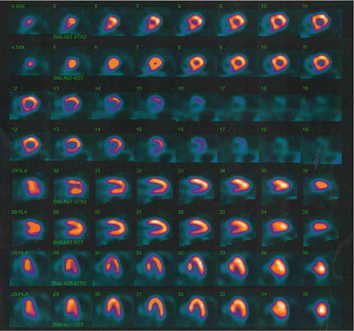
| The patient is made to walk on a treadmill or pedal on a bicycle until he reaches at least 85% of his maximum predicted heart rate. When the exercise is stopped, an injection containing a radioactive substance is given. This radioactive substance is delivered by blood flowing through the arteries to the heart. If a vessel supplying blood to a particular part of the heart is blocked, less or none of this substance will reach that part of the heart. The patient is then scanned with a machine that detects the radioactive substance. Unequal distribution of the radioactive substance (perfusion defect) is indirect evidence that blockage is present in one or some of the arteries. |
|
| If the test is abnormal, a second scan is performed the next day to see if the perfusion defect is reversible. An irreversible defect indicates a scar or dead muscle is present. A reversible defect indicates that the muscle is alive but deprived of blood during exercise. |
|
| An abnormal test means that a coronary angiogram should be performed to confirm if blockage is present. |
|
| IMAGE FROM A STRESS PERFUSION SCAN |
|
 |